CHEMOTHERAPY COST IN INDIA
/0 Comments/in Cancer, Treatments /by HTIIndia is one of the fastest-growing medical tourism destinations, offering the best cancer treatment at a low cost. Every year, foreign and national cancer patients are treated with chemotherapy in India. It varies widely based on the specific medications used and the number of cycles necessary to treat Cancer. Nonetheless, chemotherapy costs in India are reasonable, and the best drugs and specialists are readily available. This mostly sends medical tourism patients to India from affluent nations such as the United States, Europe, and the Middle East, as well as countries with little resources such as Bangladesh, Africa, Sri Lanka, Iraq and Middle Eastern countries like Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan.
Chemotherapy for Cancer Patients in India is one of the reasons patients migrate to India since the most up-to-date medications are accessible there.
Chemotherapy is a critical treatment that can help patients combat Cancer. This detailed guide will shed light on how much chemotherapy costs in India, giving you a comprehensive understanding of the expenses involved. From the cost of different chemotherapy drugs to the fees charged by oncologists and hospitals, we will delve into every aspect of treatment expenses. By providing this information, we aim to empower you to make informed decisions about your healthcare journey. With cancer cases on the rise globally, it is essential to have a clear picture of the financial implications of chemotherapy. Whether you are an individual seeking treatment options or a caregiver supporting a loved one, understanding the costs can help you plan better and explore various avenues for financial assistance, such as insurance coverage or government schemes.
How much does chemo cost in India? Why do foreigners ask the most asked questions?
The answer to the most asked question is in this article. Whether you are an individual seeking treatment options or a caregiver supporting a loved one, understanding the costs can help you plan better and explore various avenues for financial assistance, such as insurance coverage or government schemes.
Cost: – Chemotherapy costs in India can vary greatly based on several factors, including the kind of cancer, the precise medications and treatment plan provided, the location of the treatment center, whether the patient is getting chemotherapy as an outpatient or inpatient, and if the patient is domestic or internationally. Furthermore, the patient’s health insurance coverage, if relevant, may have an impact on the cost.
Chemo sessions sometimes take a few weeks or months as per the patient’s intake condition. Usually, it is completed within one month.
Per session cost – 300$ to 2000$ for international patients. The cost mentioned above includes cancer types, city, chemo center or hospital, and tests.
Depending on the kind of Cancer, the approximate chemotherapy cost might range between Rs 3,000,00 and Rs 20,000,00 (US$ 3000 TO US$ 30,000).
Chemotherapy is administered through IV (intravenous chemotherapy), with costs ranging from 70,000 ($1,000) to 1,05,000 ($1,500).
Oral chemotherapy is another popular method of delivery; oral chemotherapy costs $56,000 ($800) in India.
Chemotherapy port prices start at $210,000 ($3,000) since little surgery is required, therefore the expenses are greater. These fees, as well as any subsequent treatments, are included in a package.
What is Chemotherapy?
It is a medical word that refers to the treatment of Cancer. Chemo refers to a drug that is used in this therapy to stop the new generation of cancer cells. Chemotherapy medications are intended to target and harm rapidly proliferating cells, including cancer cells. They can, however, disrupt healthy cells that divide fast, such as those in the bone marrow, hair follicles, and the gastrointestinal tract lining. This can result in hair loss, nausea, and a compromised immune system. Chemotherapy is usually given systemically, which means it circulates throughout the body via the bloodstream. This enables it to target cancer cells throughout the body, including those not visible or accessible by surgery.
It is one of the primary treatment techniques, alongside surgery, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy, depending on the kind and stage of Cancer.
Types
More than a hundred different medicines are used in cancer chemotherapy. While all chemotherapy medications cause cell damage, they attack various cell targets at different stages of the cell cycle. Combining medications that destroy the cancer cells in different ways can improve the treatment’s effectiveness.
Depending on the kind and the treatment plan, chemo medications can be delivered in a variety of methods, including oral tablets, intravenous (IV) infusion, intramuscular injection, or directly into a specific body cavity.
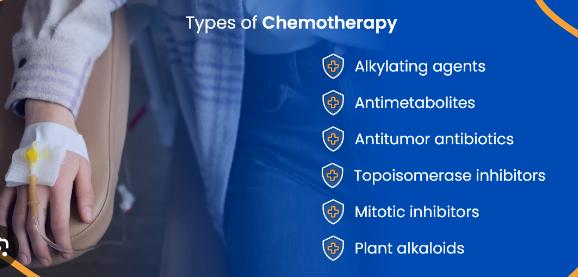
The main types of chemotherapy:
- Alkylating agents
- Antimetabolites
- Anti-tumour antibiotics
- Topoisomerase inhibitors
- Mitotic inhibitors
- Plant alkaloids
Other medications that cure Cancer outside chemotherapy include hormone therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted treatment. Oncologists may employ chemotherapy in conjunction with another type of medicine in a patient’s treatment regimen. These medications are treated in different ways, and their adverse effects are typically distinct from those of chemotherapy. Discuss with your medical staff what to expect from your specific medicines.
Hormone therapy is in which certain hormones are removed, blocked, or added to the body. It is also known as endocrine treatment or hormonal therapy.
Immunotherapy: – is another method of treatment in which the body’s immune system is used to recognize, target, and eliminate cancer cells. Immunotherapy has shown promise in the treatment of several forms of Cancer. It has 4 types of therapy.
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: – These medications inhibit immunological responses by targeting proteins on the surface of immune cells or cancer cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors work by removing the “brakes” on the immune system, allowing it to target cancer cells more efficiently. Pembrolizumab, nivolumab, and ipilimumab are a few examples.
- CAR T-Cell Therapy: – T-cell treatment entails genetically altering a patient’s T cells (a kind of immune cell) to express receptors capable of recognizing particular proteins in cancer cells. When these modified T cells are injected back into the patient, they target and destroy cancer cells. CAR T-cell therapy has been extremely effective in treating blood malignancies such as leukaemia and lymphoma.
- Cytokines: – Interferons and interleukins are cytokines that can activate the immune system to target cancer cells.
- Cancer Vaccines: – Cancer vaccines boost the immune system to recognize and target antigens associated with cancer. Some vaccinations are intended to prevent while others are intended to treat it.
Hormone Therapy: – Hormone treatment is used to treat hormone-sensitive malignancies by inhibiting hormone effects or lowering hormone production. It is also known as endocrine therapy; a cancer treatment that includes tampering with the body’s hormonal balance to delay or stop the growth of hormone-sensitive malignancies. It is mostly used to treat breast and prostate cancer, although it may also be useful in other hormone-dependent malignancies.
Here are several examples:
- Tamoxifen (breast cancer treatment)
- Leuprolide (prostate cancer treatment)
- Aromatase inhibitors (for the treatment of breast cancer)
Types of Hormone Therapy:
Anti-estrogen treatment: This hormone treatment is to treat women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors (such as anastrozole, letrozole, and exemestane) are examples of such medications. Tamoxifen inhibits estrogen activity, but aromatase inhibitors diminish estrogen production in postmenopausal women.
- Anti-Androgen Therapy: – Prostate cancer is treated with anti-androgen treatment. It includes medications such as bicalutamide, enzalutamide, and abiraterone. These medications inhibit the effects of androgens (male hormones such as testosterone) on prostate cancer cells.
- LHRH: – These medications, such as leuprolide and goserelin, are used to treat prostate cancer. They suppress testosterone levels in males by inducing an increase in hormone production (a flare) at first, then gradually decreasing hormone production.
- Selective Oestrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): These medications, like tamoxifen, can have estrogen-like actions in some tissues while acting as anti-estrogen in others. They are used in the treatment of breast cancer.
- SARMs (Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators): SARMs, such as enobosarm, are emerging therapies for prostate cancer that target androgen receptors on cancer cells.
Targeted Chemotherapy: – also known as targeted chemotherapies, are cancer treatments that target specific chemicals or processes involved in cancer cell development and dissemination. Unlike typical chemotherapy, which may harm both diseased and healthy cells, targeted treatments are meant to specifically target and destroy cancer cells. This accuracy may result in fewer adverse effects and, maybe, improved efficacy in treating specific forms of cancer.
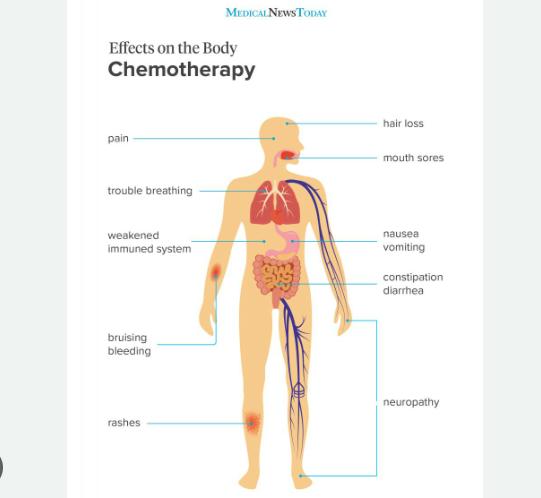
Side Effects of Chemotherapy
- Nausea- light meals after the procedure are advised because they may cause nausea.
- Vomiting- some drugs may cause nausea effects. Vomiting cannot be considered a disease and cannot create any type of pain. It can cause weakness due to excess water loss.
- Diarrhea- it is advised to take low-calorie foods because of weak digestion after the treatment. Diarrhea is a condition where watery tools are used more than once time in a day. It is a common problem and lasts a short time.
- Hair loss- people may experience hair loss due to drugs. In some cases, facial hair or eyebrows are temporary.
- Mouth sores- some treatment drugs may cause mouth ulcers, wounds, or infections due to radiation therapy.
- Bleeding problems- in the chemotherapy process, blood components like platelets drop as bleeding problems may occur after a minor cut.
- Infertility- It may reduce libido which causes an inability to produce offspring.
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!